A hockey puck with a mass of 0.16 kg is a common sports object. Understanding its properties can enhance your hockey knowledge.
Hockey pucks are essential in the game of ice hockey. They are small, dense, and designed for fast, smooth movement on ice. Weighing 0. 16 kg, a standard puck is crucial for maintaining the game’s speed and control. The weight affects the puck’s speed, trajectory, and how players handle it on the ice.
Knowing these details can help both players and fans appreciate the skill involved in the sport. In this blog, we will explore the significance of a hockey puck’s mass, its impact on gameplay, and why it matters in the world of hockey. Let’s dive in!

Credit: askfilo.com
Introduction To Hockey Puck Physics
Hockey is a fast-paced and thrilling sport. The puck is crucial in every match. Understanding the physics behind it can enhance your appreciation of the game. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of hockey puck physics.
Properties Of A Hockey Puck
A hockey puck is more than just a piece of rubber. Its properties influence the game’s speed and control. The standard puck is made of vulcanized rubber and has a diameter of 76.2 mm and a thickness of 25.4 mm. It weighs around 0.16 kg.
Here are some essential properties of a hockey puck:
- Material: Vulcanized rubber
- Diameter: 76.2 mm
- Thickness: 25.4 mm
- Weight: 0.16 kg
Mass And Its Importance
The mass of a hockey puck, 0.16 kg, plays a vital role in its performance. A puck’s mass affects its momentum and speed. It also influences how it interacts with the stick and the ice.
Here is a table summarizing the impact of mass on different aspects of the game:
| Aspect | Impact of Mass |
|---|---|
| Momentum | Higher mass increases momentum |
| Speed | Mass helps maintain speed on ice |
| Control | Optimal mass allows better control with the stick |
In summary, the mass of 0.16 kg is designed to balance speed and control. It ensures an exciting and competitive game.
Forces Acting On A Hockey Puck
A hockey puck is a small, round object used in the sport of hockey. It has a mass of 0.16 kg. When players hit the puck, several forces act on it. These forces determine how the puck moves on the ice. Understanding these forces can improve your gameplay.
Friction And Resistance
Friction is a force that opposes the puck’s motion. When the puck slides on the ice, it encounters friction. The ice surface reduces friction, making the puck glide smoothly. This is why hockey is played on ice.
Besides friction, air resistance also affects the puck. As the puck moves, air pushes against it. This force is usually small but can slow the puck down. The combined effect of friction and air resistance determines how far the puck travels.
Impact Of Player’s Force
When a player hits the puck, they apply a force. This force propels the puck forward. The speed and direction of the puck depend on the force applied. A stronger hit sends the puck faster and farther.
The angle at which the player hits the puck also matters. Hitting the puck at different angles changes its path. Players use this to their advantage during the game.
In summary, understanding the forces acting on a hockey puck helps in better control and strategy during the game. Keep practicing to master these skills!
Motion And Trajectory
Understanding the motion and trajectory of a hockey puck is essential. It helps in analyzing its movement on the ice. A hockey puck with a mass of 0.16 kg follows specific physical principles. These principles guide its speed, direction, and path.
Newton’s Laws Of Motion
Newton’s laws of motion play a crucial role in understanding the puck’s behavior. The first law states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This means a hockey puck will not move unless hit by a stick.
The second law explains that the force applied to an object equals its mass times its acceleration. For a 0.16 kg puck, a greater force results in faster acceleration. The third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. When a player hits the puck, the puck exerts an equal force back on the stick.
Calculating Trajectory
Calculating the trajectory of a hockey puck involves understanding its initial velocity and angle. The angle at which the puck is hit determines its path. A higher angle results in a higher, longer arc. A lower angle keeps the puck closer to the ice.
Friction between the puck and the ice affects its motion. Ice provides minimal resistance, allowing the puck to glide smoothly. The puck’s speed decreases over time due to this friction. External forces, like wind or player interference, also alter the puck’s trajectory.
In summary, the motion and trajectory of a hockey puck are governed by physical laws. Understanding these principles helps in predicting the puck’s path and improving gameplay strategies.
Credit: www.numerade.com
Energy And Momentum
The physics of a hockey puck involve energy and momentum. These principles determine how the puck moves on the ice. Understanding them can enhance your appreciation of the game.
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. A hockey puck with a mass of 0.16 kg gains kinetic energy as it moves. The faster the puck moves, the more kinetic energy it has. This energy depends on both the mass and speed of the puck.
For example, a puck sliding across the ice at high speed has significant kinetic energy. This energy is what gives the puck its ability to travel long distances. It is also what makes it difficult to stop.
Conservation Of Momentum
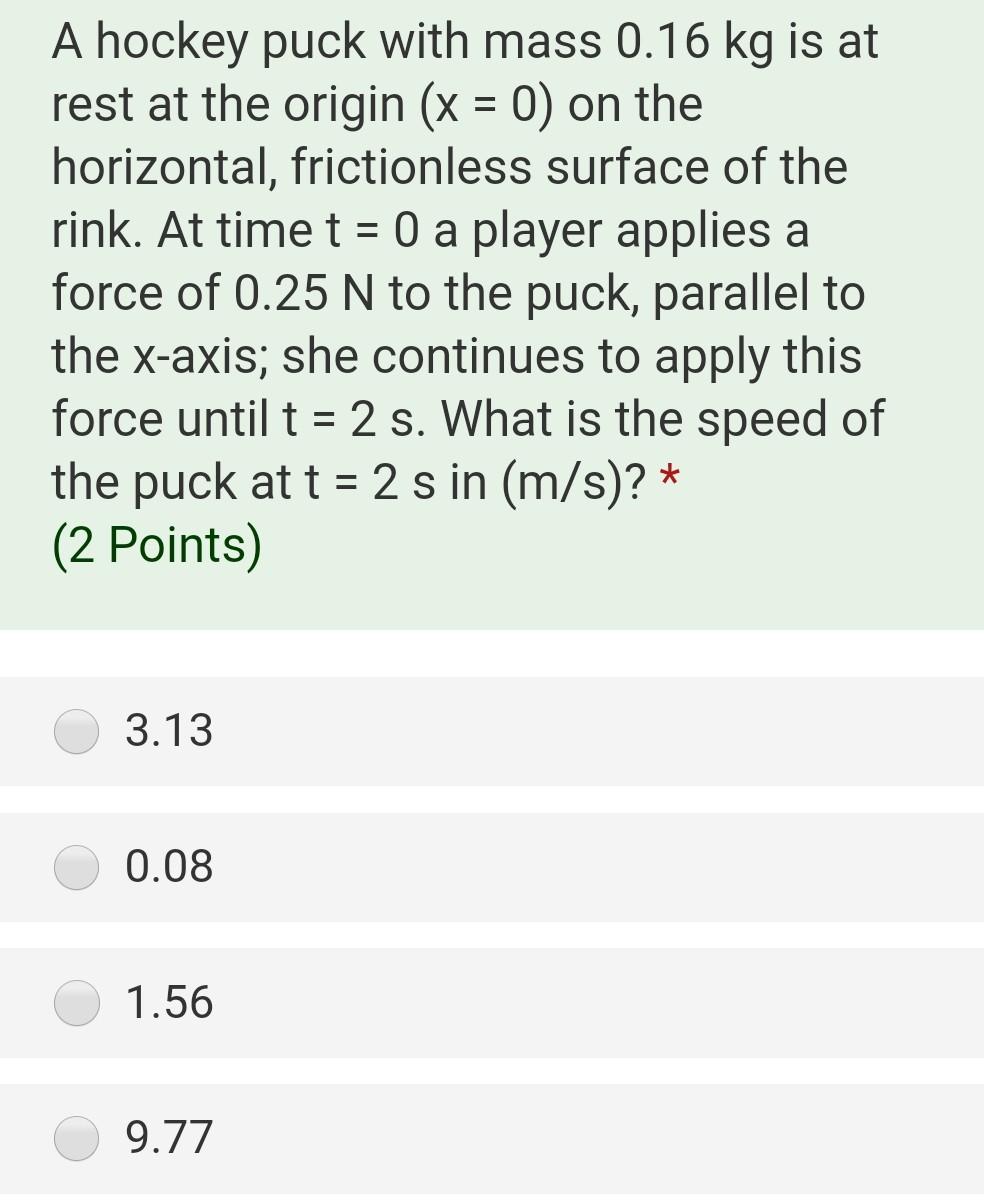
Momentum is the product of mass and velocity. A moving hockey puck has momentum. When players pass the puck, they transfer momentum. This is the principle of conservation of momentum.
During a game, the total momentum before and after a collision remains the same. If two pucks collide, their combined momentum remains constant. This principle helps explain the movements and interactions on the ice.
Energy and momentum are key to understanding hockey physics. They explain how pucks move and interact. This knowledge can deepen your understanding of the sport.
Practical Applications
A hockey puck with a mass of 0.16 kg plays a vital role in the game. This small object impacts various aspects of hockey. From training to equipment design, understanding its applications helps players and coaches improve their game.
Training And Strategy
The 0.16 kg hockey puck is essential for effective training. Coaches use it to teach players about puck control and shooting accuracy. For instance, players practice with pucks of different weights. This helps them adapt to various game situations.
Strategies also revolve around the puck’s mass. Teams plan their moves based on the puck’s speed and trajectory. Knowing how the puck behaves helps players anticipate and react quickly. This knowledge is crucial during fast-paced games.
Equipment Design
The design of hockey equipment is influenced by the puck’s mass. Sticks, for example, are made to withstand the force of a 0.16 kg puck. The materials used and the stick’s design ensure durability and performance.
Skates also play a role. They are designed to provide stability and control. The 0.16 kg puck’s movement on ice requires skates to offer precise maneuverability. Proper skate design helps players maintain balance and speed.
Even protective gear is designed with the puck’s mass in mind. Helmets, pads, and gloves are tested to absorb impact. This keeps players safe during intense games.
Credit: www.chegg.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Mass Of A Hockey Puck?
A standard hockey puck weighs 0. 16 kilograms.
Why Is A Hockey Puck 0.16 Kg?
This weight ensures the puck moves smoothly on the ice.
How Heavy Is An Ice Hockey Puck?
An ice hockey puck typically weighs 0. 16 kg.
What Material Is A Hockey Puck Made Of?
Hockey pucks are made of vulcanized rubber.
How Does Puck Weight Affect The Game?
A 0. 16 kg puck ensures consistent play and safety.
What Are The Dimensions Of A Hockey Puck?
A hockey puck is 1 inch thick and 3 inches in diameter.
Why Is Puck Weight Important In Hockey?
The weight ensures the puck is stable and controllable.
Can The Weight Of A Puck Vary?
No, professional pucks weigh 0. 16 kg for standardization.
How Does Puck Mass Impact Player Performance?
The 0. 16 kg weight allows for precise shots and passes.
Conclusion
Understanding the mass of a hockey puck helps improve gameplay skills. A 0. 16 kg puck offers consistency and predictability. Knowing the puck’s mass allows better control and accuracy. This knowledge can aid both beginners and seasoned players. Practice with this standard puck to enhance performance.
Remember, mastering basics leads to greater success. Keep learning and stay dedicated. Enjoy the game and keep pushing your limits. Hockey is both challenging and rewarding.



